-
The glomerulus is a filter
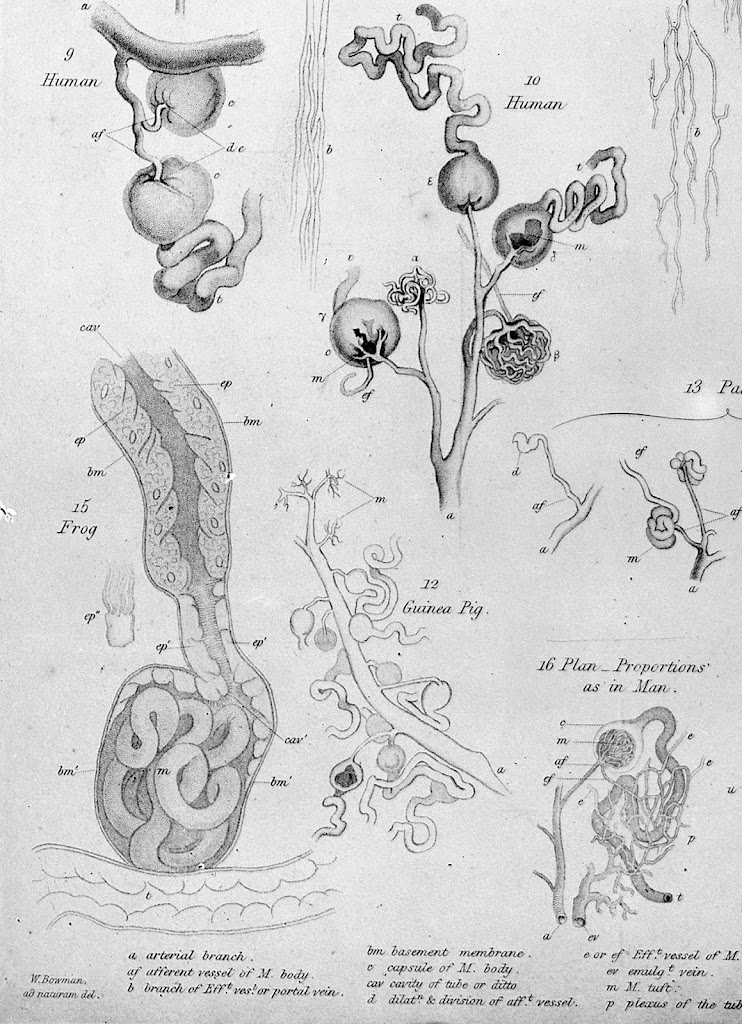
Physiologists resolve an anatomical impasse, 1924 Illustrations of Malpighian bodies, from Bowman 1842, Philosophical Transactions 132: 57-80 (p78). Wellcome Library (M0011305) – Creative Commons licence Malpighi spots glomeruli, 1666The first microscopes emerged in the Netherlands in the 1600s, early discoveries being associated with Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in the Netherlands, Robert Hooke in England, and Marcello…
-
Acute nephritis in 1875
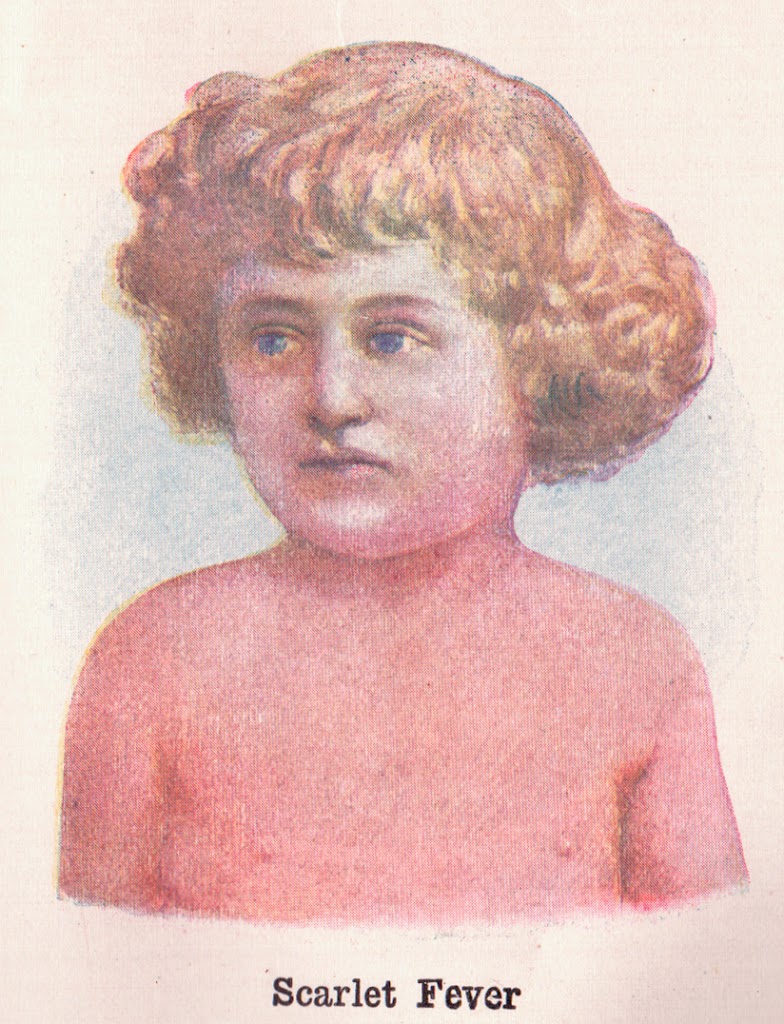

50 years after Bright Richard Bright’s 1827 report created the discipline of nephrology and triggered an exciting period of clinical research into kidney disease. William Howship Dickinson (1832-1913) was one of these early nephrologists, employed at Great Ormond St Children’s Hospital in London. In addition to an interest in neurology he wrote a notable three-part…
-
Richard Bright and the discovery of kidney disease
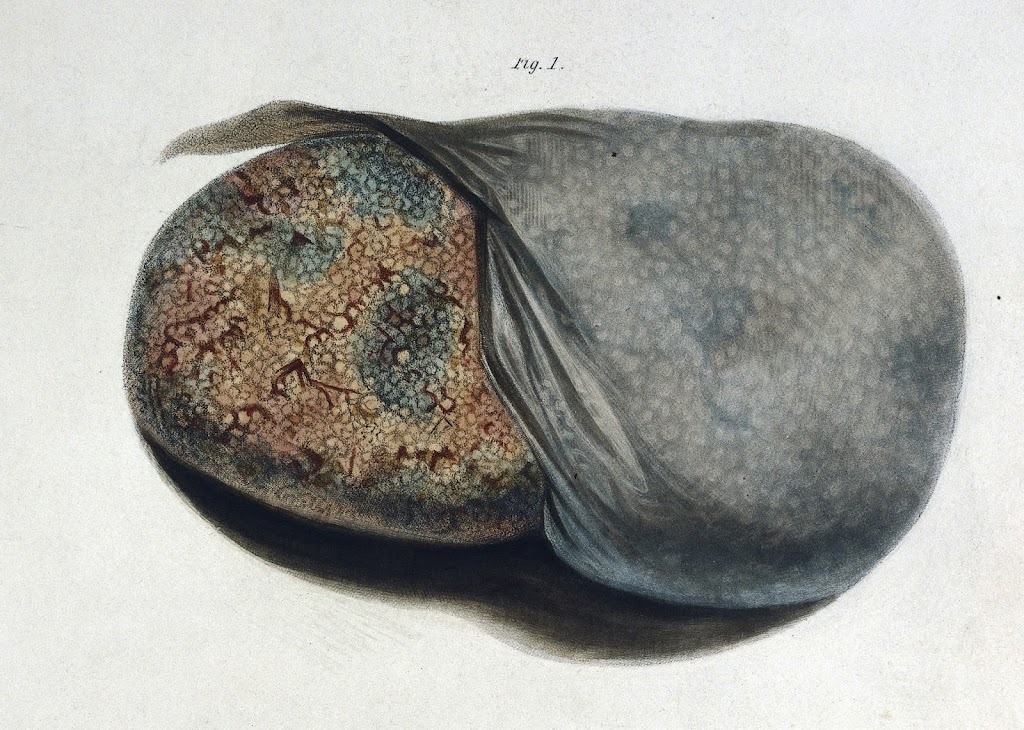

Nephrology is born, 1827 Fig 1 from Bright 1827. (Wellcome Images) Richard Bright (1789-1858), is widely regarded as the founder of the specialty of nephrology. He gave his name to Bright’s disease, which was used for over 100 years first as a term for any type of kidney disease, and later particularly for glomerular diseases.…
-
Lithotomists: the first nephro-urological specialists
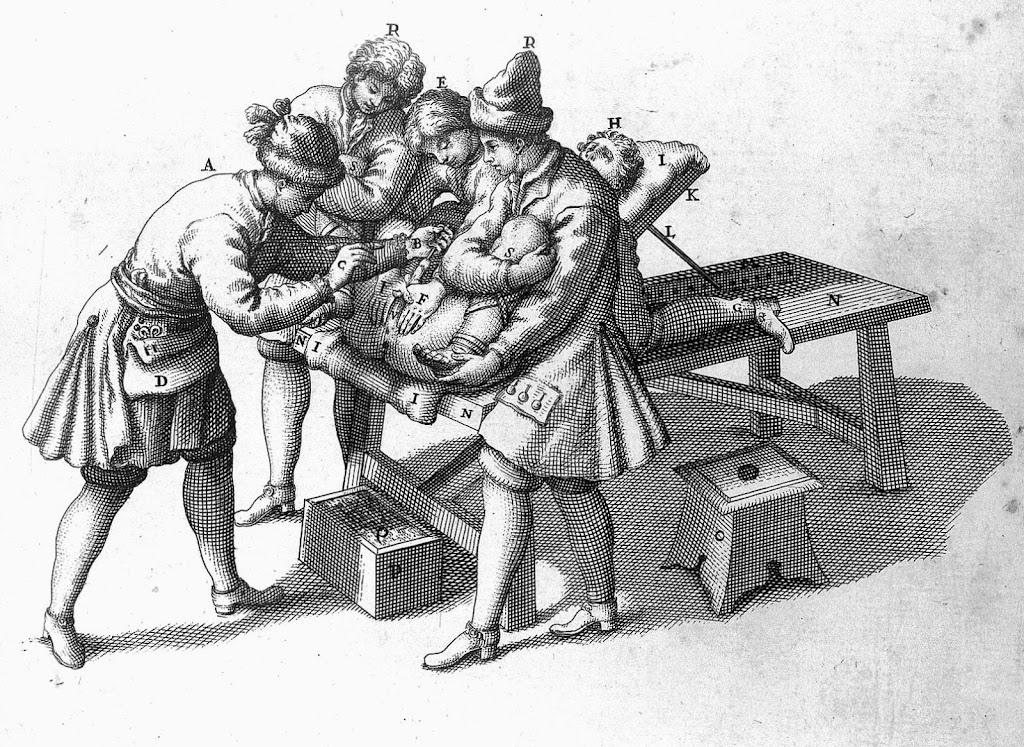
A sound has been passed from the penis into the bladder. With the genitalia held out of the way, and the patient strapped firmly to the table and held down by strong men, the surgeon cuts down onto the sound through an incision in the perineum. The incision is then widened a little, and the stone grasped…
-
Marathon nephritis and postural proteinuria
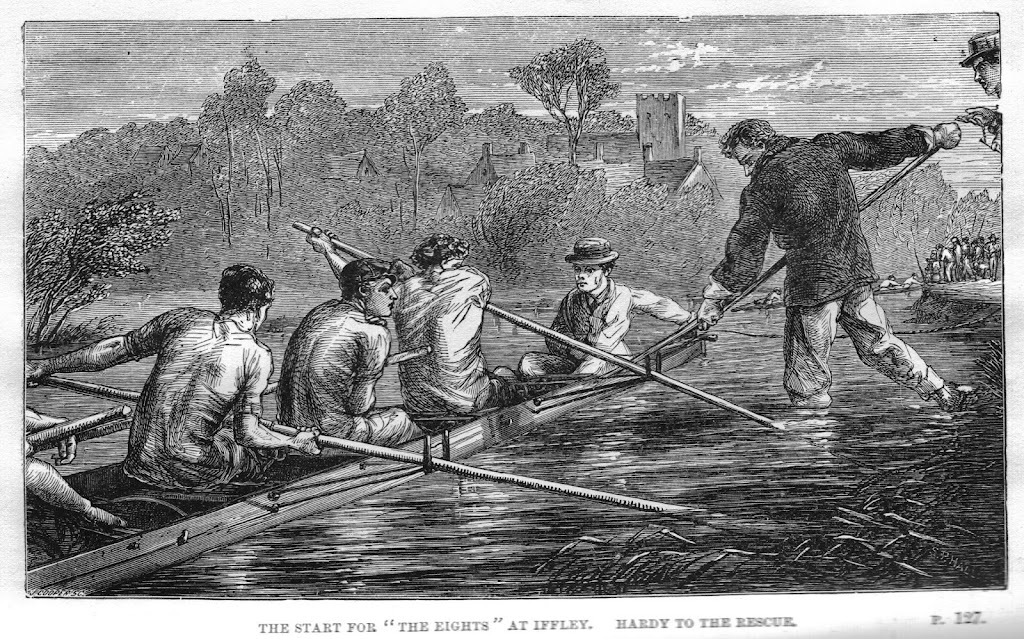

When urinary abnormalities don’t indicate renal disease From Tom Brown at Oxford (1861) illust Sydney P Hall (1903 edition) Richard Bright’s 1827 description of the association of proteinuria with dropsy and serious kidney disease led to doctors of the 1800s kitting up with apparatus to test for proteinuria, long before they could measure blood pressure. Uroscopy…
-
Lead nephropathy
The oldest interstitial renal disease? Lead pipe in Roman Bath. (Wikimedia Commons, see foot) Severe abdominal colic and gout caused by lead poisoning was described by Nikander in Ancient Rome. Acute poisoning also causes nerve palsies, particularly wrist-drop, encephalopathy, fits and sometimes death. Many patients became ill over weeks or months, with associated anaemia, malaise,…
-
Monkey glands and the science of renal hypertension
Quack medicine and technology contributed to the discovery of Renin in 1898 A 1928 advert exploiting the Monkey Gland craze. Source In 1889 the renowned scientist Brown-Sequard at the age of 72 publicly recounted how how he felt rejuvenated after injecting himself with extracts of animal testis. This led to an extraordinary wave of quack…
-
Blood pressure is linked to kidney disease in the 1870s
Revealed by Mahomed’s sphygmograph The discovery of hypertension and its linkage with renal disease came remarkably late. Richard Bright (1836) observed that “the hypertrophy of the heart seems, in some degree, to have kept pace with the advance of disease of the kidneys”. But he had no way to measure blood pressure, and even by…
-
The invention of the dipstick
Test papers to dipsticks in 72 years The SSA test came first. From Cornell Vet School, with permission* For urinary protein detection the basic chemistry was established in the late 1700s, and until the late 1950s the standard test was still based on acidification and/or heating of urine to precipitate protein. Carrying bottles of acid…
-
The invention of IV fluid therapy
Thomas Latta first used IV saline in the 1832 cholera epidemic IV infusions at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary in the 1970s The second worldwide pandemic of cholera hit Scotland in 1832, travelling to Europe on ships from India, hence ‘Asian cholera’. This was – and remains – a terrible illness with a high mortality without medical…
-
Dropsy, nephrosis, nephrotic syndrome
The first effective treatment for a kidney disease, 1950. Dropsy is an ancient word (first recorded about 1290 AD) meaning oedema. Generalised oedema can be caused by heart or liver or kidney disease, or by malnutrition. In all of these it was a pretty bad sign in ancient medicine as it meant that the patient…